Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Reports
- Ruptured Massive Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cured by Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Ji Eun Lee, Joong-Won Park, In Joon Lee, Bo Hyun Kim, Seoung Hoon Kim, Hyun Beom Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):154-159. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.154
- 2,914 Views
- 62 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
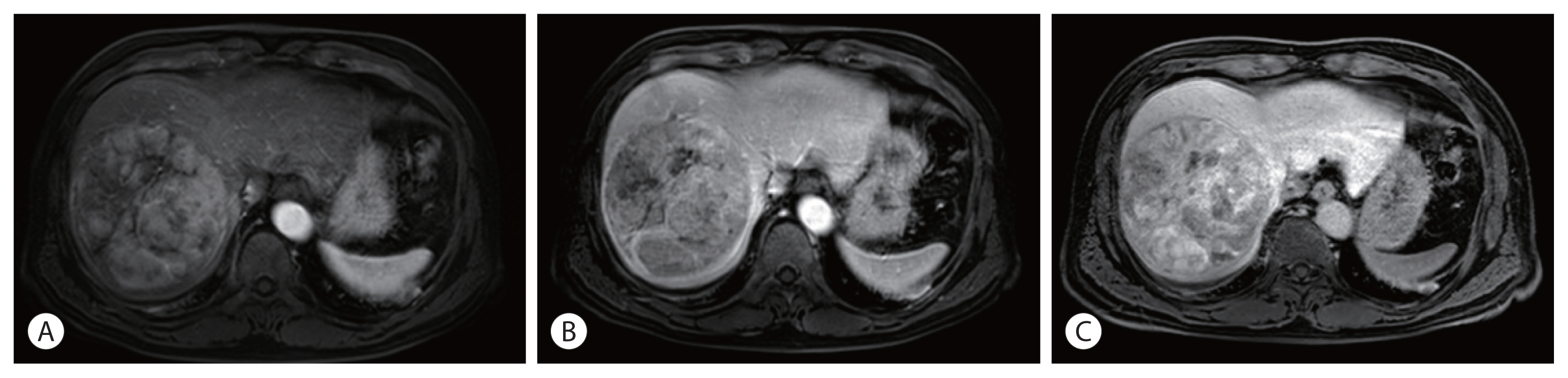
PDF - Spontaneous tumor rupture is a serious but rare complication of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has a low survival rate. Here, we report a case of massive HCC that ruptured and was treated successfully with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). A 55-year-old man with abdominal pain was diagnosed with a 12-cm-wide ruptured HCC at segment 8. The overall liver function was scored as Child–Pugh A, but the single nodule tumor had ruptured; therefore, TACE treatment was initiated. After the first TACE treatment, residual tumors were found; thus, secondary TACE was performed 5 months later. No new lesions or extrahepatic metastases were found 16 months after the first TACE treatment, so hepatic resection was performed for curative treatment. The postoperative pathology results did not reveal any cancer cells; hence, TACE alone resulted in a cure. We report this case because the cure has been maintained for more than 3 years after resection.

- A Case of Spontaneous Rupture of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Supplied by the Right Renal Capsular Artery Treated by Transcatheter Arterial Embolization
- Joo Yeon Jang, Ung Bae Jeon, Jin Hyeok Kim, Tae Un Kim, Hwaseong Ryu, Mong Cho, Young Mi Hong, Maeran Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):59-63. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.59

- 5,087 Views
- 87 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We present a case of spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma with poor liver function managed by transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE). The patient’s bilirubin level was 2.1 mg/dL, albumin level was 2.4 g/dL, and prothrombin time international normalized ratio was 2.1. In addition, the patient had also developed a large number of ascites. The tumor was supplied by the right renal capsular artery, as observed on angiography. With successful TAE, no hepatic failure occurred. We believe TAE can be a safe and effective treatment option, even in patients with poor liver function, if tumors are supplied only by extrahepatic collateral vessels.

Review Article
- Emergencies in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Chang Wook Kim, Chang Don Lee
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(1):1-7. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.1.1
- 868 Views
- 13 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may be suffered by various emergency conditions such as spontaneous rupture of HCC with intraperitoneal hemorrhage, variceal bleeding with portal vein tumor thrombus, hemobilia, obstructive jaundice, distant metastasis of HCC in central nervous system, spinal bone metastasis of HCC with cord compression and so on. These emergencies can be categorized into 4 types, conditions with spontaneous rupture of HCC, distant metastasis of HCC, direct invasion of HCC and paraneoplastic syndrome. According to HCC status and liver function, some these patients showed more beneficial effects with active palliative treatments than with best supportive cares. Various palliative treatments can be used such as surgical resection, transarterial chemoembolization, radiotherapy, systemic chemotherapy and combination of above therapies. We reviewed the emergencies in patients with HCC for improving survival and quality of life.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter