Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- The effect of nucleos(t)ide analogues on clinical outcomes of patients treated with transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jae Min Park, Won Hyeok Choe, Jeong Han Kim, So Young Kwon, Byung Chul Yoo
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):155-162. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.22
- 3,341 Views
- 90 Downloads
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Because hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication has been known to play an important role in cancer recurrence after curative treatment of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), we examined whether treatment based on nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs) might decrease the recurrence rate and improve patient survival.
Methods
The retrospective cohort study enrolled 73 patients with chronic hepatitis B who were treated with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) with curative intent for HCC. Among those, 30 and 43 patients were treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and entecavir (ETV), respectively.
Results
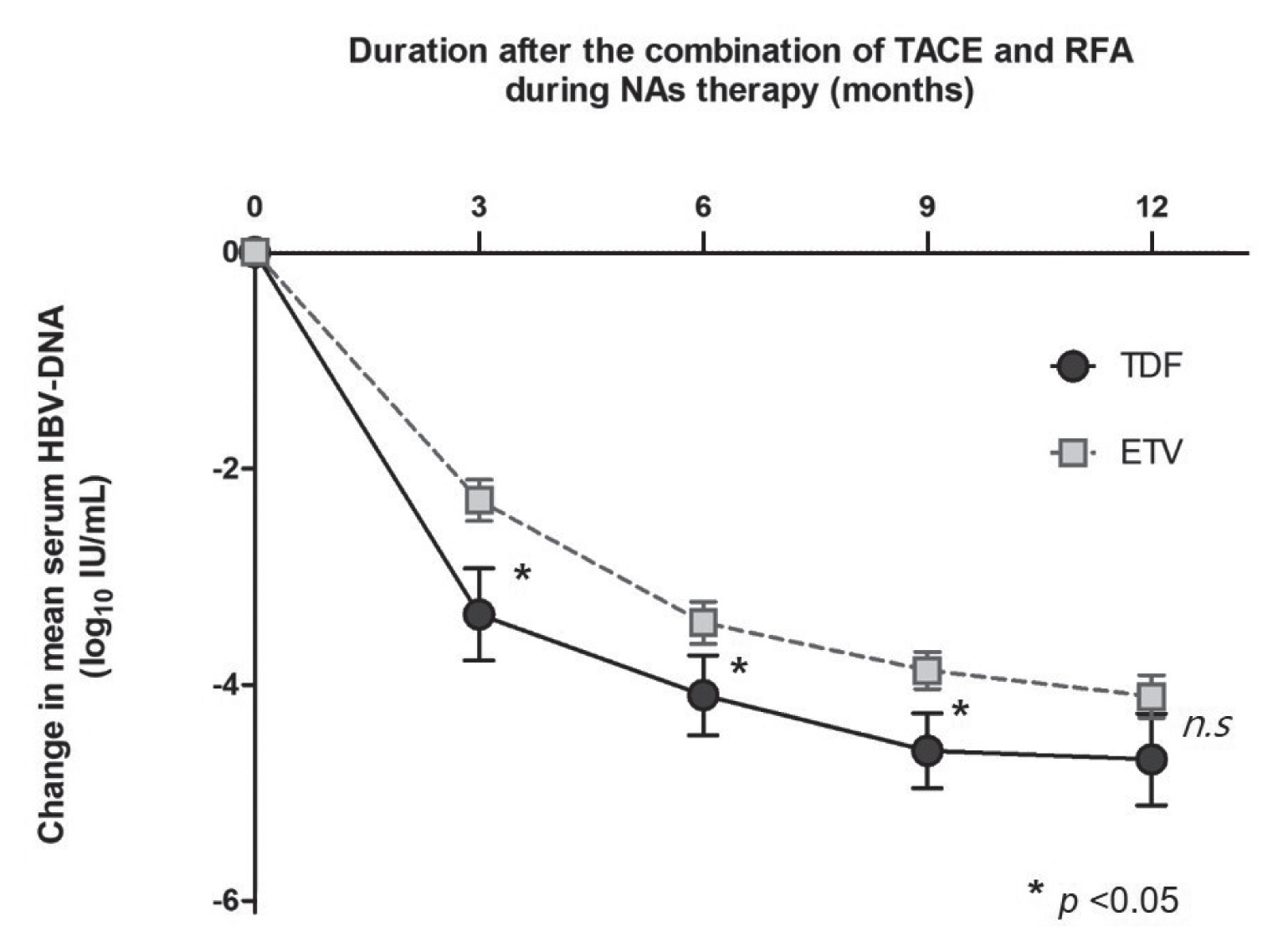
Of the 73 patients, 51 experienced HCC recurrence, and 14 patients were dead during a follow-up of 73±34 months. Multivariate analyses showed that tumor size (hazard ratio [HR], 1.590; 95% confidence-interval [CI], 1.106-2.285; P=0.012) and Child-Pugh class B (vs. class A/non cirrhosis; HR, 5.794; 95% CI, 2.311-14.523; P=0.001) was significantly associated with HCC recurrence, and Child-Pugh class B (HR, 7.357; 95% CI, 2.100-25.777; P=0.002) was an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for survival. During NAs therapy, TDF was superior to ETV for complete viral response at 1 year after the date of combination of TACE and RFA (P=0.016). However, the risks of HCC recurrence and survival were not significantly different between those treated with TDF versus ETV.
Conclusions
TDF was superior to ETV for achieving complete viral response. However, the recurrence and mortality after TACE and RFA for HBV-related HCC were not significantly different between patients treated with TDF versus ETV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced prognosis of HCC patients undergoing radical treatments with tenofovir versus entecavir: A meta-analysis based on propensity score matching studies
Qingyan Kong, Mengshi Yi, Fei Teng, Zheyu Chen
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024; 47(1): 55. CrossRef - Tenofovir versus entecavir on the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hui Liu, Cheng-Long Han, Bao-Wen Tian, Zi-Niu Ding, Ya-Fei Yang, Yun-Long Ma, Chun-Cheng Yang, Guang-Xiao Meng, Jun-Shuai Xue, Dong-Xu Wang, Zhao-Ru Dong, Zhi-Qiang Chen, Jian-Guo Hong, Tao Li
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 17(6): 623. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Enhanced prognosis of HCC patients undergoing radical treatments with tenofovir versus entecavir: A meta-analysis based on propensity score matching studies


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter